Functional Analysis Talk
From wiki
Why do functional analysis?
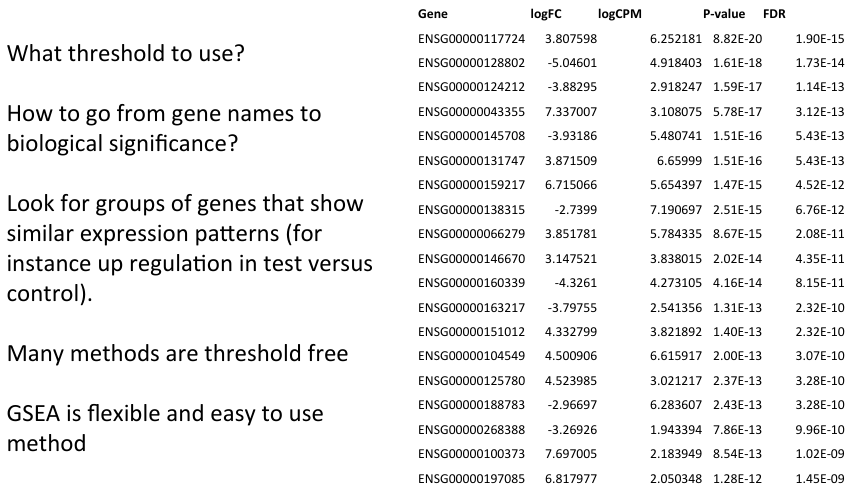
- Statistical significance is not the same as biological significance
- Variety of methods available to compare functional annotation to gene data
- General aim is to identify gene functions/categories that show an interesting expression profile
- Potentially identify genes with smaller but biologically significant changes.
Functional analysis methods
- Positional Gene Enrichment – looks for regions of chromosome showing changed expression.
- The Ingenuity Pathways Analysis (IPA)
- Several methods use Gene Ontology (GO) terms or other "gene sets"
- GO is the means by which we identify function.
- Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
- GOAL: Gene Ontology AnaLyzer
- GOrilla
A functional analysis method
First order by measure of DE

Compare to list

Move through each gene 1

Move through each gene 2

Highest Level identified

Repetition of Process

Further shufflings

Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
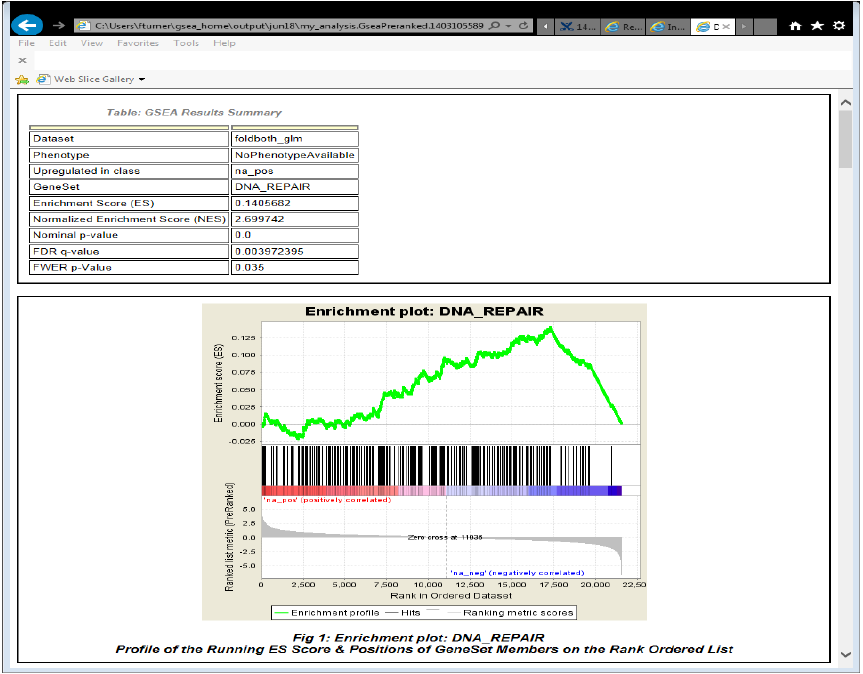
- Example GSEA report of a gene set found to be enriched among down regulated genes in cancer samples
Conclusions
- A wide variety of methods are available for functional analysis of expression data
- Aids biological interpretation of the data
- Different types of annotation can be compared to expression data.
- Many methods do not require user specified thresholds
Further reading
- Eden et al "GOrilla: a tool for discovery and visualization of enriched GO terms in ranked gene" BMC Bioinformatics 2009
- Volinia et al "GOAL: a software tool for assessing biological significance of genes groups" Nucleic Acids Res 2004
- Tamayo, et al."Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles" PNAS 2005
- Preter et al "Positional gene enrichment analysis of gene sets for high-resolution of overrepresented chromosomal regions" Nucleic Acid Research 2008
- http://www.ingenuity.com/products/ipa








