Difference between revisions of "Estimating Gene Count Talk"
(Created page with "Estimating gene count = Estimating Gene Count = How many reads are overlapping genomic features? - or - Can we confidently assign each read to a feature/transcript/gene? Not...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Estimating Gene Count = | = Estimating Gene Count = | ||
How many reads are overlapping genomic features? | How many reads are overlapping genomic features? | ||
| Line 17: | Line 15: | ||
= Multi mapping reads = | = Multi mapping reads = | ||
* Unsolved problem: | * Unsolved problem: | ||
| − | + | :- this can account for 10-30% of reads | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:unsolved.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | * Ignore them, but then again this decreases sensitivity | |
| − | * | + | * Weighted assignment |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Of course, longer reads would solve this problem. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | = One transcript, one set of reads = |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:t1.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | = Two transcripts, another set of reads = | |
| − | + | [[File: t1t2.png | |
| − | = | + | = Aggregation to Gene-level 1 = |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:tt1t2aggreg.png]] | |
| − | = | + | = Third transcript, another set of reads = |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:t1t2t3.png]] | |
| − | + | = Aggregation to Gene-level 2 = | |
| − | + | [[File:t1t2tt3aggreg.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | = HTSeq-count = | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:htseq.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Designed for RNA-Seq counting | * Designed for RNA-Seq counting | ||
| Line 103: | Line 55: | ||
= HTSeq-count = | = HTSeq-count = | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:htcats.png]] | ||
= Probabilistic approach = | = Probabilistic approach = | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 9 May 2017
Contents
- 1 Estimating Gene Count
- 2 Multi mapping reads
- 3 One transcript, one set of reads
- 4 Two transcripts, another set of reads
- 5 Aggregation to Gene-level 1
- 6 Third transcript, another set of reads
- 7 Aggregation to Gene-level 2
- 8 HTSeq-count
- 9 HTSeq-count
- 10 Probabilistic approach
- 11 Probabilistic approach
- 12 Probabilistic approach
- 13 Probabilistic approach
Estimating Gene Count
How many reads are overlapping genomic features? - or - Can we confidently assign each read to a feature/transcript/gene? Not so simple.
We also have:
- Multi mapping reads
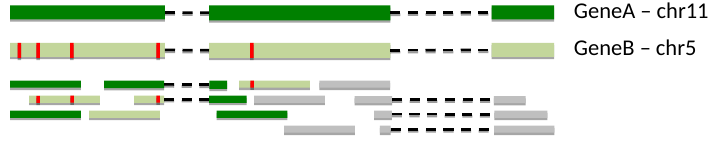
- Overlapping genes/transcripts
Two approaches:
- Focus on what’s known with certainty
- Probabilistic
Multi mapping reads
- Unsolved problem:
- - this can account for 10-30% of reads
- Ignore them, but then again this decreases sensitivity
- Weighted assignment
Of course, longer reads would solve this problem.
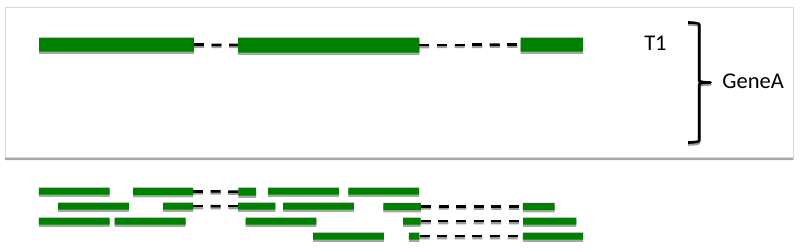
One transcript, one set of reads
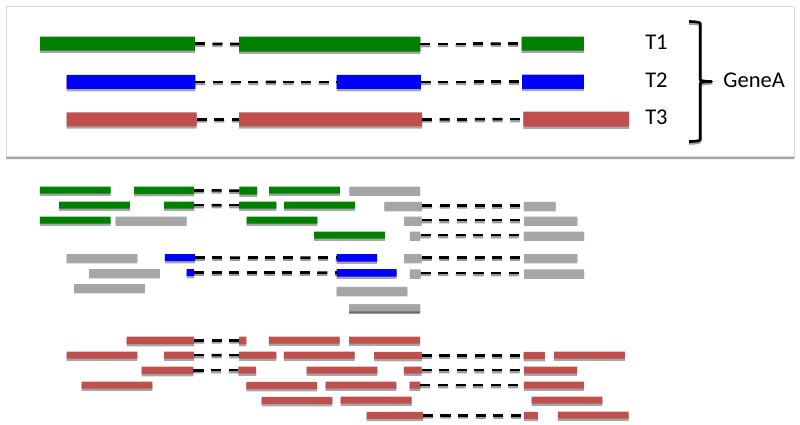
Two transcripts, another set of reads
[[File: t1t2.png
Aggregation to Gene-level 1
Third transcript, another set of reads
Aggregation to Gene-level 2
HTSeq-count
- Designed for RNA-Seq counting
- Simple to use (especially since v0.6.0)
- Work at gene level
- Remove multi-mapped reads
- Several modes to resolve remaining uncertainty
HTSeq-count
Probabilistic approach
Cufflink
cuffdiff
Probabilistic approach
Cufflinks: Reconstruct the transcripts from the data and annotation
Probabilistic approach
Cufflinks: Reconstruct the transcripts from the data and annotation
Cuffdiff: Assign each read/fragment to a transcript with a probability maximum likelihood.
Probabilistic approach
Cufflinks: Reconstruct the transcripts from the data and annotation Pros: - Better methodology - Integrated package (ease of use) Cons: Cuffdiff: - Do not support alternative experiment design - History of heterogeneous results/versions
- Assign each read/fragment to a transcript with a probability maximum likelihood.