Quality of Mapping Talk
Contents
Mapping quality control
Some issues are only detectable in the context of the genome:
- Duplicate reads
- Fragment size distribution
- Gene coverage
- Completeness of data
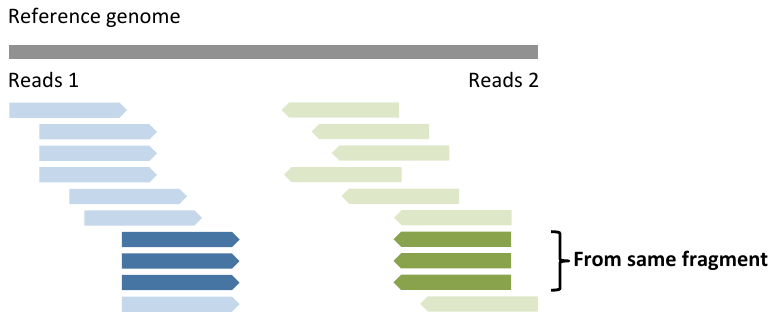
Duplicate reads
- Only detectable with paired end reads
Duplicate reads 2
- Duplicates can be PCR artefacts
- Duplicates can be real, from highly expressed transcripts
- For RNA-seq, removing duplicates is still being debated
- We don’t remove them, but it’s important to:
- - assess the duplicate rate
- - determine whether the duplicate rate can be explained by a few highly expressed genes
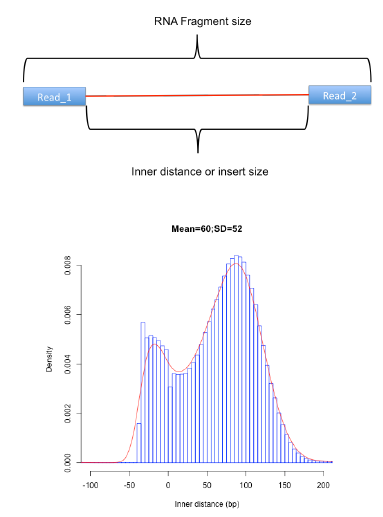
Fragment size distribution
| * Should correspond with
fragment size selected during library preparation
reads can span introns when calculating fragment size |
|
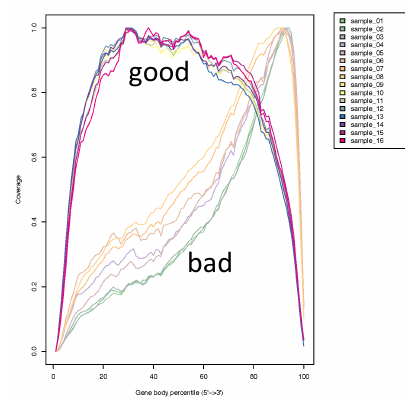
Gene coverage
| * Read coverage of the gene
should be uniform
is expected because of degradation of the RNA
3' bias |
|
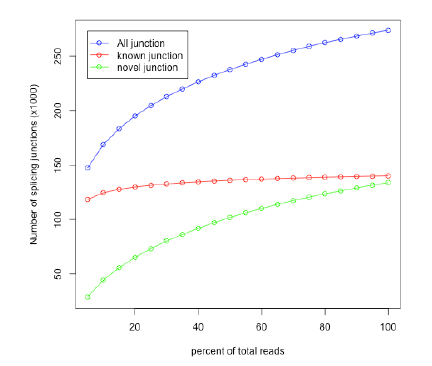
Completeness of data
- From a saturated RNASeq dataset, all known splice junctions should be rediscovered.
- Check saturation by resampling resampling 5%,10%,..,100% of alignments, detect splice junctions from each subset and compare them to reference gene models