Difference between revisions of "MinION (Oxford Nanopore)"
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
= Developments during 2016= | = Developments during 2016= | ||
| − | * Pore technology moved from R7 (had patent conflict problems with Illumina) to R9 | + | At the beginning of 2016, udring a regular run, MinION could: |
| − | * implemented new deep-learning | + | * Process 500Mb of DNA from a flow-cell |
| + | * Each pore could read 70 bases/second | ||
| + | * Accuracy still low at 70-80% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Major steps were made to improve this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Pore technology moved from R7 (had patent conflict problems with Illumina) to R9 (better throughput, higher accuracy) | ||
| + | * implemented new deep-learning algorithm | ||
| + | * closer collaboration with key academic researchers. | ||
= Links = | = Links = | ||
* Brian Naugton's [http://blog.booleanbiotech.com/nanopore_2016.html blog entry 11 Oct 2016] taking stock of recent advances | * Brian Naugton's [http://blog.booleanbiotech.com/nanopore_2016.html blog entry 11 Oct 2016] taking stock of recent advances | ||
* [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v530/n7589/abs/nature16996.html Nature paper 11 Feb 2016] describing Minion use in Ebola outbreak | * [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v530/n7589/abs/nature16996.html Nature paper 11 Feb 2016] describing Minion use in Ebola outbreak | ||
Revision as of 12:26, 2 February 2017
Contents
Introduction
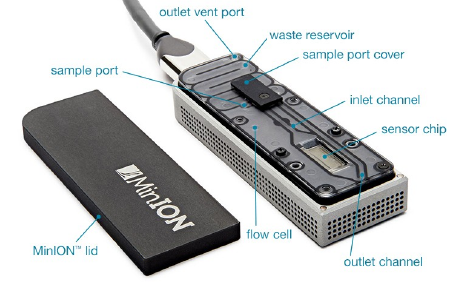
Entirely unique sequencing method, where the flowcell is inserted into a USB container, and from there, plugged into a computer.
Due to its small size in comparison with Illumina, IonTorrent and PacBio, this sequencing tool is eminently suited to field work.
Overview
Reputed advantages
- flowcell pores good for several runs, until they die out, which they may do at different times.
- Reads an be quite long ... 100kb is possible.
Shortcomings
- Computer, usually a laptop, needs to be continually connected to internet, and to be in high workload mode (no economy nor sleep mode allowed).
- accuracy at least an order of magnitude worse than Illumina (~90% vs >99%)
- Probably more expensive than Illumina on a per-base basis, although there is no service contract involved as one might expect from Illumina. Low cost of Illumina cost is largely down to economies of scale.
Characteristics
- 1D, which means single-strand reading, is the most common and mature of MinION's modes. 2D, where both strands are read, one after the other, is possible, but is more demanding and more prone to errors.
Software Round-up
The software required can be split into two groups of programs:
- Sequencing generation
- MinKNOW, for control of MinION device & run parameters
- Metrichor, for cloud basecalling of event data
- Chronolapse a screen image grabber for record keeping
- TeamViewer, for remote control of MinION computer
- MinoTour, live monitoring / control of run while sequencing (a collaboration with Matt Loose of Nottingham University).
- Sequence File Analysis
- Poretools, poRe Sequence extraction and data summaries (deevloped by Nick Loman and Aaron Quinlan (latter of bedtools fame)).
Developments during 2016
At the beginning of 2016, udring a regular run, MinION could:
- Process 500Mb of DNA from a flow-cell
- Each pore could read 70 bases/second
- Accuracy still low at 70-80%
Major steps were made to improve this:
- Pore technology moved from R7 (had patent conflict problems with Illumina) to R9 (better throughput, higher accuracy)
- implemented new deep-learning algorithm
- closer collaboration with key academic researchers.
Links
- Brian Naugton's blog entry 11 Oct 2016 taking stock of recent advances
- Nature paper 11 Feb 2016 describing Minion use in Ebola outbreak